When Leigh gravitated from his gentler comic explorations of working-class England into the starker realm of Naked (1993), Roger Ebert noted that the film “describes characters who exist in the world without the usual layers of protection. They are clothed, but not warmly or cheerfully. But they are naked of families, relationships, homes, values and, in most cases, jobs. They exist in modern Britain with few possessions except their words.”
Or, in the case of John Mallord William Turner, except paintings. The genius known as “the painter of light” and widely regarded as the precursor to Impressionism is an isolated soul despite a varied constellation of relationships. He lives with a father whom he loves and a doting housekeeper who longs for any acknowledgement of the intimacy she allows him, a simple woman who suffers an affliction of the skin. He moves comfortably among patrons in their country houses and among his fellow artists at the Royal Academy, whilst holding himself above them.
 |
| Helvoetsluys, 1832 |
Genius, solitary, disciple – Billy Turner is also nothing if not a man making a living at his work, every day, day after day. “Inspiration is for amateurs,” the painter Chuck Close has said. “The rest of us just show up and get to work.” To that end, Mr. Turner is about the process of making art: sketching landscapes in countless notebooks; stretching canvases; buying pigments and oils; mixing paints; controlling light; putting paint to canvas; displaying work; competing in the marketplace; courting patrons – all the while struggling to remain true to an inner vision.
“Painting,” says an unseen guest amidst the patter of a dinner party towards the end of Mr. Turner,” is silent poetry.” Watching Timothy Spall's incarnation of the great artist, one might feel compelled to add that painting is performance, as gestural an art as dance. Spall’s Turner muddles his brushes in palms full of paint; he spits, splatters, claws, and blows. When not painting he is traipsing and sketching, sketching and traipsing in a never-ending peripatetic quest, not merely to see nature but to be nature.
 |
| Staffa, Fingal's Cave, 1831-1832 |
Indeed, Mr. Turner is Leigh’s love letter to painting, just as Topsy-Turvy was his homage to theater. Topsy-Turvy opens in 1884, when the luminaries of London’s musical theater, recently knighted composer Arthur Sullivan and as yet untitled librettist W. S. Gilbert, have fallen out. They are repeating themselves; the plots and tropes have worn thin. Despite the failure of Princess Ida, Gilbert is content with his formulae, stubbornly refusing to see them as modi operandi at all. Sir Sullivan is well aware that they have a choice: rest on their comic opera laurels and fade into obscurity or reinvigorate the genre they created. In a happy turn of events, a reluctant Gilbert is dragged by his wife to a Japanese living exhibition in Knightsbridge, an experience that ignites the librettist’s imagination. In the ensuing scenes, The Mikado gestates and is born. We witness the process – the plain hard work of the production’s unfolding: lines to be refined, music to be rehearsed, costumes and sets to be designed then sewn and built, a vision to be realized – the flurry and chaos of it all, and then… Curtain, please!
 |
| Timothy Spall in Mike Leigh's 1999 Topsy-Turvy |
Turner grew up from tradesmen, his father a barber and wig-maker, his mother the daughter of a family of butchers and shopkeepers. When the scientist Mary Somerville visits to demonstrate her experiments with light and magnetism, Turner, by way of introduction, praises his father’s skill with razor and brush. When Mrs. Somerville suggests the son now wields the brush, Turner demurs and dismisses her with a wave of the hand.
 If we compare the structure of Leigh’s film to a gimbal, the single axis at its center is a man plying his craft, and the pair of concentric rings rotating around him are Art and Death. Everything about art figures in to Leigh’s telling, from the making to the selling to the theorizing. As contemptuous as Turner is of the art establishment represented by the Royal Academy on the one hand, and the bohemian avant-garde embodied in the effete person of critic John Ruskin on the other, he is shrewd enough to know full well he needs both. At the same time that he exhibits next to George Jones, famous for his military subjects; Irish sculptor John Carew; genre painter C.R. Leslie; and English Romantic painter Constable – Turner impishly courts controversy as his painting moves further from realism toward abstraction. Simultaneously, he enjoys Ruskin’s patronage while hardly masking his countenance as one suffering a fool. (If there is one misstep in the film, it is the unfortunate representation of Ruskin as a silly, lisping fop when in reality he was Turner's tirelessly passionate advocate. Philip Hoare of The Guardian agrees.)
If we compare the structure of Leigh’s film to a gimbal, the single axis at its center is a man plying his craft, and the pair of concentric rings rotating around him are Art and Death. Everything about art figures in to Leigh’s telling, from the making to the selling to the theorizing. As contemptuous as Turner is of the art establishment represented by the Royal Academy on the one hand, and the bohemian avant-garde embodied in the effete person of critic John Ruskin on the other, he is shrewd enough to know full well he needs both. At the same time that he exhibits next to George Jones, famous for his military subjects; Irish sculptor John Carew; genre painter C.R. Leslie; and English Romantic painter Constable – Turner impishly courts controversy as his painting moves further from realism toward abstraction. Simultaneously, he enjoys Ruskin’s patronage while hardly masking his countenance as one suffering a fool. (If there is one misstep in the film, it is the unfortunate representation of Ruskin as a silly, lisping fop when in reality he was Turner's tirelessly passionate advocate. Philip Hoare of The Guardian agrees.)
Loss hangs over Turner’s life from birth, and death redounds as a leitmotif throughout the film. As his mother became increasingly mad, ultimately committed to Bethlem Hospital in 1800, Turner was sent to live with his maternal uncle, a butcher. At 11, he attended school in Margate on the northeast coast of Kent. He would return to sketch many times, becoming a regular lodger with a Mr. and Mrs. Booth with whom we find him engaged in an evening of conversation that turns from Mr. Booth’s haunting days aboard slaving ships to Turner’s early years in Margate, whereupon Turner recalls two school mates lost to scrofula.
Turner has as little interest in his ex-mistress, Sarah Danby, and their daughters as he has in his housekeeper, Sarah’s husband’s niece Hannah. Nor does the introduction to the eldest daughter’s newborn as “Your only surviving grandchild” move him. Yet upon the death of his beloved father, the remote Turner succumbs to grief while sketching a young prostitute. Upon his return to London, he embarks on the painting Death on a Pale Horse.
Loss hangs over Turner’s life from birth, and death redounds as a leitmotif throughout the film. As his mother became increasingly mad, ultimately committed to Bethlem Hospital in 1800, Turner was sent to live with his maternal uncle, a butcher. At 11, he attended school in Margate on the northeast coast of Kent. He would return to sketch many times, becoming a regular lodger with a Mr. and Mrs. Booth with whom we find him engaged in an evening of conversation that turns from Mr. Booth’s haunting days aboard slaving ships to Turner’s early years in Margate, whereupon Turner recalls two school mates lost to scrofula.
 |
| Slavers Throwing Overboard the Dead and Dying - Typhoon coming on, 1840 |
 |
| Death on a Pale Horse, 1829 |
Leigh's is a chronicle not only of a genius and an artist but of a man growing old in a world on the cusp of dramatic change, a world in which inexorable technological advances will transform life altogether. Like Sir Arthur Sullivan, Turner longs to leave his immortal mark upon the stage and understands that to do so means the very reinvention of his medium
That wonderful range of mind of which Constable remarked is everywhere in Mr. Turner. In a world in which art and science were viewed as complementary, Turner socialized with inventors as easily as with fellow artists. He would have been familiar with Mary Somerville’s paper, The Magnetic Properties of the Violet Rays of the Solar Spectrum, perhaps even heard her present it at the Royal Society in 1826. He has extended an invitation to her to demonstrate her experiments with the prismatic spectrum and magnetism in his chambers. His delight in her discoveries is palpably clear, and James Hamilton, one of Turner’s biographers, has suggested that Mrs. Somerville’s theories influenced the violet tones and the northward orientation of his 1829 painting Ulysses deriding Polyphemus.
 |
| Ulysses deriding Polyphemus, 1829 |
In a rowing barge on the Thames, with Clarkson Stanfield and David Roberts, the three painters come upon a paddle-wheel steam tug towing the Fighting Temeraire to be scrapped in the breaker’s yard. Turner’s colleagues wax nostalgic on the noble history and ignominious end of the famed vessel of the Battle of Trafalgar. “The ghost of the past,” says one. Turner – while admiring the glories of the sail ship just as he will defend the 17th century French landscape painter Claude Lorrain when Ruskin derides him – bellows, “No. The past is the past. You’re observing the future! Smoke. Iron. Steam!” Stanfield tells Turner he should paint the scene, not knowing Turner's nascent work will become Britain’s most beloved painting.
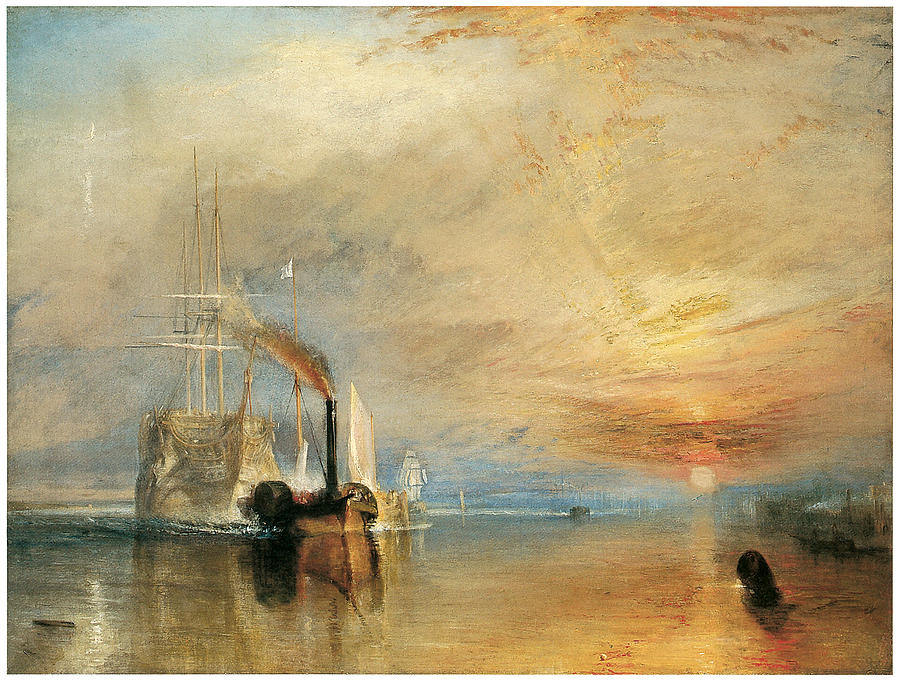 |
| The Fighting Temeraire, 1838 |
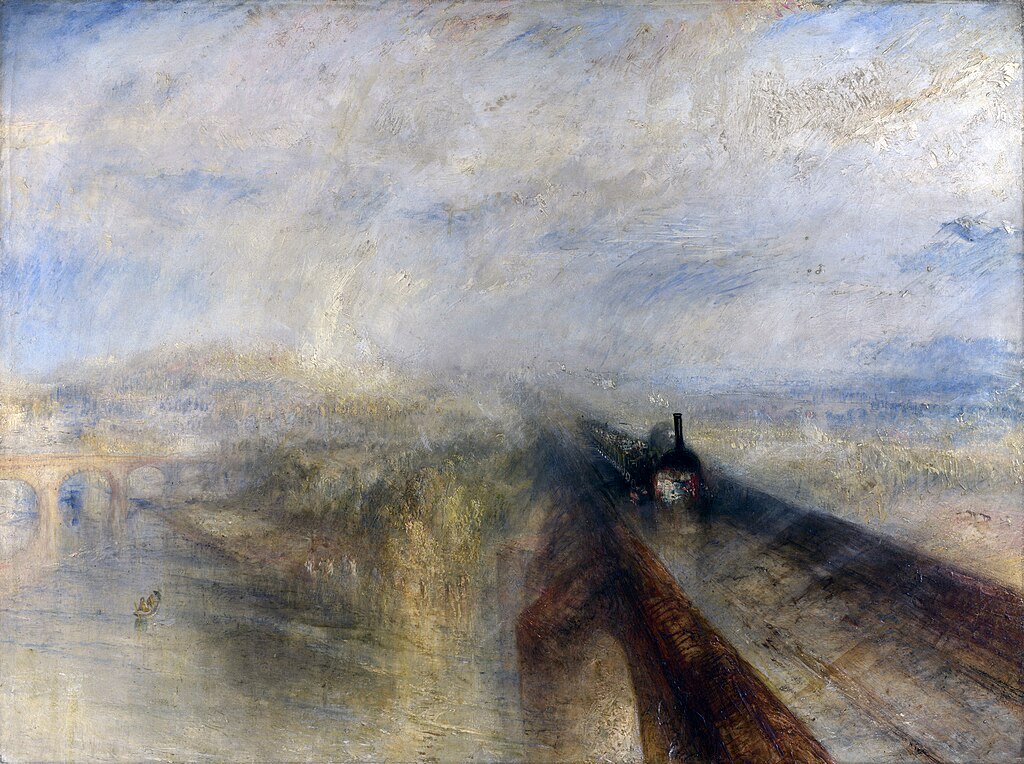 |
| Rain, Steam and Speed - The Great Western Railway, 1844 |
The precision of photography, too, will fundamentally change our way of seeing, and Leigh hints that Turner’s fascination with the new medium in all possibility could have influenced his ideas about the direction of his philosophy of painting. He has Turner visit a stereoscopic and portrait shop and have a daguerreotype made for Mrs. Booth, with whom he is now living in Chelsea. Turner asks the American photographer if the images can be made in color. When told no, he wants to know why not, to which the photographer replies, “That is a mystery.” One can’t help but wonder if Leigh is thinking about his own medium as well, for indeed, from a cinematic point of view, his Mr. Turner is a marvel.
Dick Pope’s cinematography washes the entire film in Turner’s sublime palette – all soft yellows, numinous creams, and somber greys. Each frame is perfectly composed, and unless Turner is afoot, the camera rarely travels. The scenes shot en plein air are panoramic vistas evocative of Turner's compositions, but interior shots again and again are framed by doorways that speak to a kind of compartmentalization with which Turner has structured his personal relationships as much as they provide an almost literal picture frame around the moving image.
 |
| Timothy Spall as J.M.W. Turner and Dorothy Atkinson as Hannah Danby in Mike Leigh's Mr. Turner |
Leigh says he did not “want to have faux or pastiche period music. We'd been very meticulous in the look and the detail of the film in its period accuracy, but the music, the score, should somehow be a voice that comes from a different place. It should somehow be an expression of the essence of Turner’s painting in some way.” The original score, composed by Gary Yershon, moves from the clear textures of classical music to the chromaticism of the Romantic period, then bends into modern atonalities in what might be called a sort of minimalist Romanticism. Turner is pushing his way into the pantheon through nothing less than an utter transformation of his medium, and Yershon’s music echoes the sublimity of Turner's art as well as the discordance between the artist and his world.
Leigh and Spall have given us not only a portrait of the artist as a crotchety genius, but a portrait of the artist as a working man. Art grows out of an extraordinary originality of vision but needs be from an indefatigable practice of craft. In our present age of immediacy – possessed of an indiscriminate relationship to the world that rejects mediation – where images require no making, where twitter replaces correspondence, where auto-tune substitutes for vocal artistry, where CGI replaces stagecraft – we have forgotten that it is not only a right but a responsibility to bow to hard work and discipline to develop our talents. Though the rest of us may marvel at the completed work, grace is achieved in the doing. “There's something inherently disappointing about success,” Gilbert says in Topsy-Turvy after The Mikado’s acclaim. Despite his headlong rush at immortal fame, the mortal Turner might agree.
Time passes irrevocably, Virgil said, and early in Mr. Turner we arrive at the country estate of one of Turner’s patrons, Lord Egremont, whose children’s music teacher is at the harpsicord playing a passage from Beethoven’s Pathetique. When Turner expresses his fondness for Henry Purcell, she plays “Dido’s Lament,” the suicide aria from Dido and Aeneas (c. 1688), to which Turner falteringly sings along…
When I am laid, am laid in earth, May my wrongs create
No trouble, no trouble in thy breast;
Remember me, remember me, but ah! forget my fate.
Remember me, but ah! forget my fate.


